Physical Therapy for Proximal Hamstring Injuries
Understanding Hamstring Injuries: Apophysitis vs. Avulsion Fractures
Navigating the complexities of orthopedic conditions, particularly ischial apophysitis and avulsion fractures, is crucial for young athletes. This guide aims to clarify these conditions, their impact, and the path to recovery for individuals engaged in demanding sports activities.
What is Hamstring Apophysitis?
Hamstring apophysitis involves the inflammation of the growth plate located at the ischial tuberosity, or what many refer to as the "sit bones." This condition predominantly affects adolescent athletes aged 13 to 15, as the growth plate typically closes between 16 and 23 years. Gymnasts face a higher risk due to the extreme stress placed on the hamstrings, compounded by the growth plate's vulnerability, being significantly weaker than the surrounding tendons and bones.
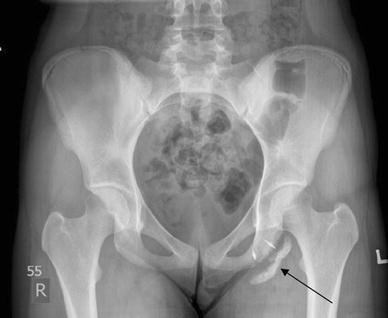
Understanding Avulsion Fractures
Contrastingly, avulsion fractures occur when a piece of bone from the ischial tuberosity is forcefully detached, often at the growth plate, during high-intensity activities like sprinting or jumping. This injury results from the sudden, traumatic stress on the hamstring muscles, presenting a distinct scenario compared to apophysitis.
Identifying At-Risk Athletes
Gymnasts, dancers, sprinters, and soccer players are particularly susceptible to these injuries. The attachment of major muscles, such as the hamstrings and adductor magnus, to the ischial tuberosity, combined with sports demanding intense flexibility and hamstring strength, increases injury risk. Recognizing early signs is essential for timely intervention.
Symptoms and Early Intervention
Key symptoms include swelling, bruising, tenderness, pain during movement, an audible pop during injury, and referred pain around the hip. Early detection and treatment are paramount, especially for athletes engaging in high-risk sports, to prevent further complications.
Rehabilitative Care
Effective physical therapy and rehabilitation for proximal hamstring injuries encompasses several phases, beginning with rest and pain management, followed by progressive strengthening exercises, and culminating in sport-specific reintegration. This phased approach ensures a holistic recovery, addressing strength, flexibility, and functional aspects.
Rehabilitation Challenges
Overlooking symptoms can delay treatment and exacerbate the condition. Distinguishing between strains, apophysitis, and avulsion fractures is critical for appropriate management, highlighting the importance of tailored rehabilitation programs and preventive measures against overuse injuries.
By staying informed and proactive, athletes, coaches, and healthcare providers can navigate the challenges of hamstring apophysitis and avulsion fractures, ensuring a safe and successful return to sport for young athletes.
References:
Frush TJ, Lindenfeld TN. "Peri-epiphyseal and Overuse Injuries in Adolescent Athletes." Sports Health, 2009.
Kujala UM, et al. "Ischial Tuberosity Apophysitis and Avulsion Among Athletes." International Journal of Sports Medicine, 1997.
Schoensee SK, Nilsson KJ. "A novel approach to treatment for chronic avulsion fracture of the ischial tuberosity in three adolescent athletes: a case series." International Journal of Sports Physical Therapy, 2014.
Papastergiou S, et al. "Apophysitis of the Ischial Tuberosity: A Case Report." Journal of Orthopaedic Case Reports, 2019.
Liu H, et al. "Avulsion Fractures of the Ischial Tuberosity: Progress of Injury, Mechanism, Clinical Manifestations, Imaging Examination, Diagnosis and Differential Diagnosis and Treatment." Medical Science Monitor, 2018.